Authors / metadata
DOI: 10.36205/trocar4.2021002
Abstract
In 2016 we introduced a new laparoscopic method for the treatment of the descensus of the uterus and vagina at our clinic. As an alternative to sacropexy, pectopexy was implemented. With this retrospective single-center follow-up analysis of all patients operated on for prolapse from September 2016 to October 2017, we evaluated the results. All had a laparoscopic pectopexy using a mesh (PRP 3×15 Dynamesh). The retrospective cohort study included 27 patients who presented to our clinic with uterovaginal prolapse POP-Q stages III and IV. 23 patients completed a two-year observation period. The laparoscopic pectopexies were all performed by the senior surgeon. There was one serious complication (3.7%). It was a bladder injury that occurred intraoperatively. There were no postoperative complications. Unexpected findings were a benign adnexal cyst, grade 1 endometrial carcinoma in a morcellated uterus, and complex hyperplasia in a morcellated uterus. As a concomitant operation, 3 patients required simultaneous posterior colporrhaphy, 1 patient had simultaneous laparoscopic paravaginal repair.
Results
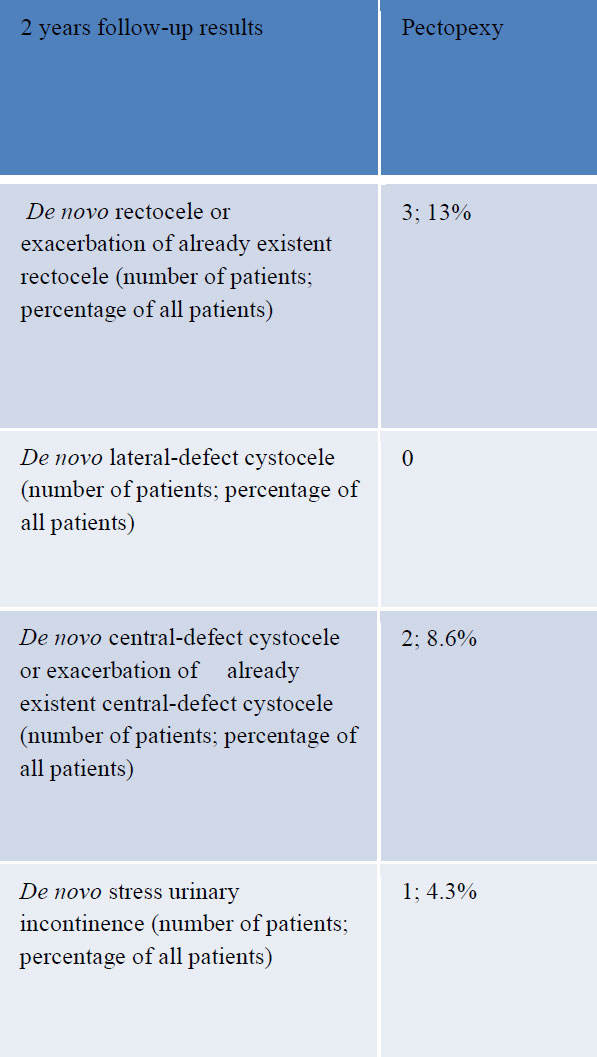
In 3 cases (13%) there was a relapse of the apical descent – due to elongation of the cervix. De novo urgency occurred in 2 cases (8.6%). In 3 cases (13%) we registered a de novo rectocele or exacerbation of an already existing rectocele. In 2 cases (8.6%) we found a de novo central cystocele or progress of an existing cystocele. In one case (4.3%) the patient reported de novo stress urinary incontinence.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic pectopexy is a good and safe alternative to laparoscopic sacrocolpo or sacrohysteropexy. It is effective and shows no bowel movement disorders or meh problems with a low recurrence rate during the two-year follow-up. Even with a small volume, similarly good results as in comparable large studies could be achieved. With the pectopexy we were able to expand our portfolio for our patients with another safe method.
Introduction
Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP) is a health problem for half of postmenopausal women who have given birth. It affects millions of women worldwide (1).
Apical prolapse refers to the descending of the vaginal apex, uterus, or cervix and can be associated with a variety of symptoms, including tissue bulging (bulge), pelvic pain, dyspareunia, and impaired sexual intercourse.
Further clinical symptoms are residuals after urination, irritable bowel syndrome, urinary incontinence, obstructive defecation and urge to defecate [2].
Sacral colpopexy is an established method for correcting apical prolapse. Although it is able to approximate the physiological axis of the vagina, this method also carries some serious operative risks [3]. Laparoscopic pectopexy is a technique, which was first described in 2010 as an alternative to sacrocolpopexy. It is based on a bilateral attachment to the Pectineal Ligament (Cooper), an extension of the lacunar ligament which runs along the pectineal line of the pubic bone [2]. The material used for suspension is a non-absorbable polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) monofilament mesh (DynaMesh® PVDF, 3 × 15 cm). This is attached to Cooper’s ligament on both sides with a non-absorbable Ethibond 0 stich and centrally to the vagina, cervix or uterus with an absorbable monofilament stitch (e.g. PDS 2/0),[Video 1].
The technique of Laparoscopic Pectopexy was first published by G. K. Noé in Dormagen, Germany [4]. Our introductory approach consisted of an initial clinical attachment in May 2016 with Professor Noe. Approval was gained by both the Clinical Governance Committee and Medical Director of Ninewells University Hospital, Dundee, as well as Health Improvement Scotland. We then invited Professor Noe to Dundee where three cases of laparoscopic pectopexy were performed under direct supervision in September 2016.
Follow – up audits were conducted at six months and two years after completion of the twelve-month period after surgery. Laparoscopic Pectopexy was submitted to the National Institute for Health and Care Evidence (NICE) as a new interventional procedure, but the procedure was stopped by NICE on the 14th of March 2018 due to a lack of supporting evidence [6]. A randomized control trial was set up comparing laparoscopic sacrohysteropexy to laparoscopic pectopexy under a research umbrella as per the NICE recommendation.
Method
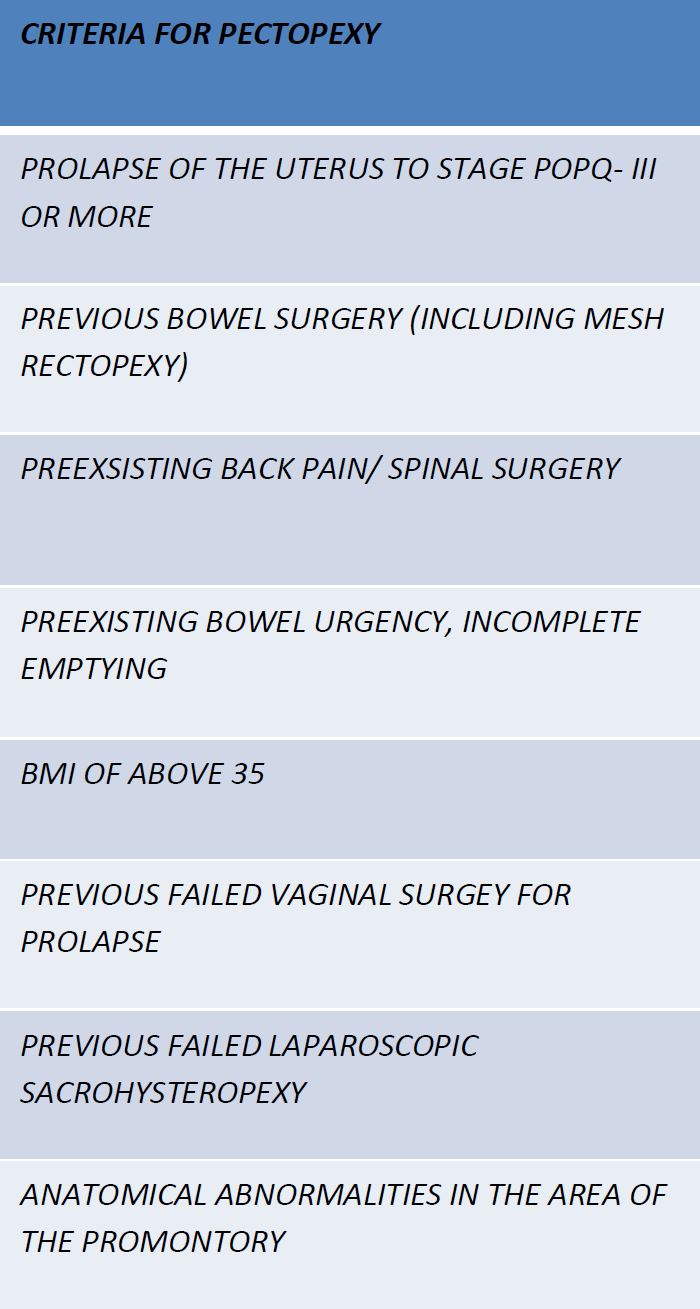
A single-center retrospective cohort study of the outcomes of all patients who underwent Laparoscopic Pectopexy using DynaMesh PRP 3×15 tailored implants made of PVDF between September 2016 and October 2017. Medical records were identified via the OPERA electronic database. Data was extracted from medical notes regarding symptoms, operative morbidity and therapeutic outcomes. The POP-Q scoring system was employed to objectively assess pre- and postoperative pelvic organ prolapse. Complications were categorized as either early or late (Clavien – Dindo classification). Quality of life was assessed using the ICIQ-VS questionnaire. Information was collated in an Excel spreadsheet for further analysis. The following inclusion criteria were used [Table1] to select patients where we felt laparoscopic pectopexy offered an advantage over laparoscopic sacrohysteropexy.
Results
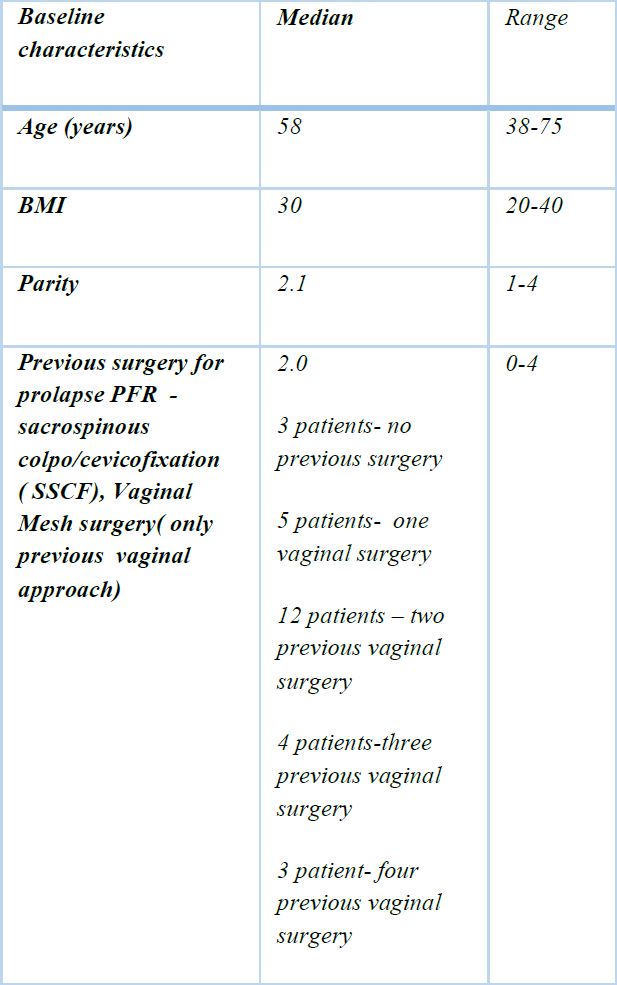
All patients who underwent Laparoscopic Pectopexy were evaluated but only 23 completed the two-year observation period. The total cohort of 27 patients was included in the assessment of perioperative complications. Baseline characteristics of the patients were assessed which demonstrated a median age of 58 and a median BMI of 30 [Table 3 patients required a concomitant posterior colporrhaphy, and 1 patient a laparoscopic paravaginal repair. The only intraoperative complication was a bladder injury fortunately there were no post-operative complications. Unexpected findings included a benign adnexal cyst, a Grade 1 endometrial carcinoma and endometrial hyperplasia in pathology specimens [Table 3].
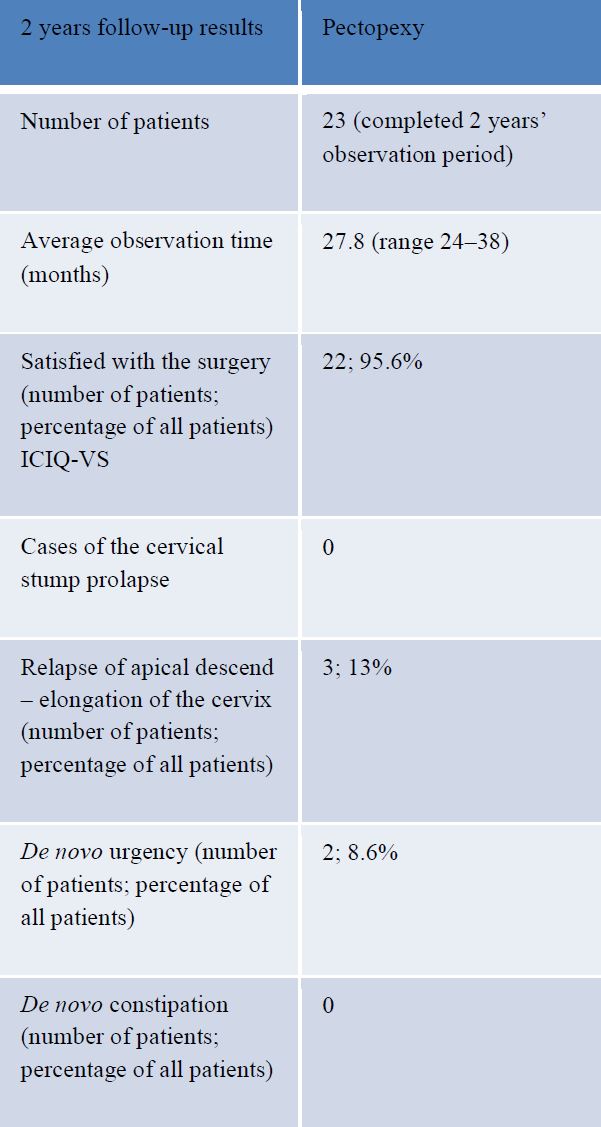
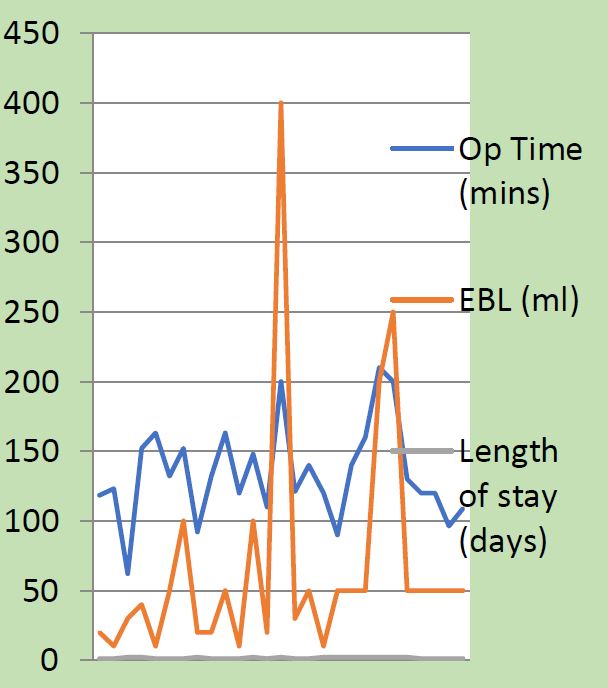
In 3 cases (13%) of the patients who completed 2 years of follow-up there was recurrence of the apical prolapse due to elongation of the cervix. De novo bladder urgency was reported in 2 cases (8.6%), a De novo rectocele or deterioration of a pre-existing rectocele was reported in 3 cases (13%). A De novo central defect cystocele or exacerbation of a pre-existent cystocele was reported in 2 cases (8.6%) and De novo stress urinary incontinence in 1 case (4.3%). 95% of patients were satisfied with the results of the surgery based on their ICIQ-VS score [Table 4, 5]. Mean operating time was 132 minutes and mean blood loss was 57mls [Fig 1].
Discussion
Laparoscopic Pectopexy has been evaluated in randomized trials as well in multicenter trials so far and appears to be safe and effective with minimal risk of complications [10-14]. The development of a cystocele, central defect or deterioration in an existing anterior wall prolapse seen in 8.6% of our patients was comparable to 7.1% seen in one randomized controlled trial. The development of a rectocele or exacerbation of an existent rectocele in 9.5% and 13% respectively was also comparable [4, 5]. De novo defecation disorders secondary to injury of the hypogastric nerves was rare and de novo stress urinary incontinence was seen in 4.3% of our patients compared with 4.8% in the randomized controlled trial [4].
Injury to the urinary bladder occurred in one patient and was minor in character (5 mm defect) and occurred in a patient with an isthmocele and co-existing endometriosis. The Repair required double layer suturing and the patient was discharged home the following day with an indwelling catheter on free flow for six days.
An interesting observation was seen in relation to the 3 laparoscopic hystero-pectopexies, two of which were performed using an anterior attachment and one using a posterior attachment to the cervix. In all cases, the patients developed a significant elongation of the cervix which required a subsequent amputation of the cervix. The point of attachment between the mesh and uterus did not alter the position of the uterus in the pelvis. In al cases surgery successfully restored the apical position of the uterus. The Suture material used to attach the mesh to the uterus (or cervix) was non absorbable multifilament-Ethibond 0, and to the vagina was monofilament, absorbable-PDS 2/0. [Video 2, 3].
Complex hyperplasia of the endometrium with an associated normal endocervical biopsy was treated conservatively. The endometrial cancer which was discovered in the morcellated uterus required subsequent removal of the cervix and re-attachment of the DynaMesh to the apex of the vagina. This was done in two separate stages three months apart to avoid mesh erosion [ Video 4, 5]. Following this incident a policy was introduced requiring an endometrial sample to be obtained and reposted prior to morcellation of the uterus during a subtotal hysterectomy.
Second look six month later for laparoscopic ventral mesh rectopexy (VMR) revealed the presence adhesions of the sigmoid colon to the central part of the apex (attachment of the mesh to the cervix) and left flank of the pelvis [Video 6].
This is likely related not to the type of surgery itself but to the material used to close peritoneum- barbed V-Loc 3/0 [7,8]. On the positive note, Laparoscopic pectopexy does not limit the access to the promontory and posterior vaginal wall in the case of the subsequent VMR which is beneficial in comparison with laparoscopic sacrohysteropexy.
Laparoscopic pectopexy does not reduce volume of the pelvic space and does not appear to be complicated by defecation disorders [Table 6].
There are several evidences on the improvement of the quality of life after laparoscopic pecopexy.
Aybike and others quoted improvement of P-QOL score, which is the quality-of-life scale of prolapse, 83.45 ± 8.7 (64–98) in preoperative patients and 8.61 ± 6.4 (0–23) in postoperative patients [9]. The results were similar to our outcome of 95.6% of satisfaction rate on ICIQ-VS. Laparoscopic pectopexy appears to be a useful new procedure in the management of apical prolapse supported by studies of the developing center and an increasing number of additional research [10-14]. It offers a more conservative approach in patients wishing to preserve fertility and gives bilateral support at the level of paracervical ring. According to the data it is highly sufficient with a low risk for the patients proven by a huge multi center trial [11].
Video’s
Conclusion
- Laparoscopic pectopexy is a good alternative to laparoscopic sacrocolpo/hysteropexy.
- Laparoscopic pectopexy is an effective, safe technique. No defecation disorders or mesh related problems were demonstrated during the two-year follow-up period.
- There were no cases of recurrence of apical prolapse at the attachment point of the mesh.
- All cases of pectohysteropexy developed significant elongation of the cervix and required subsequent surgical correction which needs to be emphasised during the consenting process.
References
Table 1: Preferred inclusion criteria for Laparoscopic Pectopexy
Table 2: Retrospective cohort study includes 27 patients with utero-vaginal prolapse POP-Q stages III and IV who underwent Laparoscopic Pectopexy between September 2016 and October 2017 by the same surgeon.
Table 3: Results for 27 patients included in the study
Table 4: Results for 23 patients completed the two-year observation period.
Table 5: Results for 23 patients completed the two-year observation period.
Fig.1: Results for 27 patients included in the study