Authors / metadata
DOI: 10.36205/trocar1.2022006
Abstract
Objective: A case report of using hysterescope for the extraction of the vagina foreign body with an intact hymen.
Methods: Case Report
Results: A 36-year-old woman presented with discomfort after masturbating with a ballpoint, and the cap was left in her vagina. The gynecological examination revealed an intact hymen and vaginal discharge. Abdominal ultrasound revealed a foreign body in the vaginal cavity. The patient was given an analgesic suppository, and a vaginoscopy was performed using a hysteroscope. The ballpoint cap was found to be in a horizontal position in the anterior and clamped using a foreign body grasper by changing its position from horizontal to vertical position. It was successfully extracted, sized of 50 x 8 x 8 mm. The patient was discharged with the intact hymen. Conclusion: Vaginoscopy is an endoscopic observatory diagnostic procedure that is important in diagnosing and evaluating the presence of foreign bodies. In addition to maintaining the integrity of the hymen, vaginoscopy can improve visualization of the vaginal cavity and increase flexibility in obtaining samples and removing the foreign body.
Introduction
Gynecological problems do occur in children, adolescents, adults, and the elderly. Reports on the management of gynecological cases in children and women who are still virgins is limited. This is related to the fragile hymenal tissue, which is easily torn. The hymen is a very valuable anatomicla entity for women because it poses as a sign related to a history of sexual activity or sexual violence. The integrity of the hymen is proof of a woman’s virginity .1 The status of a woman’s virginity is very important, especially for unmarried women, due to the relation of the value of women’s perceptions and self-esteem especially in the Muslim community.1 Vaginoscopy is performed using a hysteroscope with a diameter of 5 mm, and the entire procedure is performed without compromising the anatomicla integrity of the hymen, so it is considered an appropriate method to maintain hymenal integrity.2
Vaginoscopy is indicated for diagnosing and treatment related to bleeding and suspicion of a foreign body, neoplasm, or congenital anomalies. Vaginoscopy is considered a convenient, safe, fast and efficient method for diagnosis and management.3.4
Currently, vaginoscopy can not only be done in hospitals requiring hospitalization but can also be done in private clinics in an office setting. In private clinical settings, vaginoscopy is reported to have many advantages as compared to the operating room vaginoscopy because it does not require hospitalization, preoperative examination, and general or regional anesthesia, and reduces postoperative recovery time and costs. Complications may occur, such as cervical tears and tubal rupture, due to distension fluid.4 However, there are also reports of failures related to vaginoscopy in the office setting due to patient’s discomfort including severe pain, anxiety and embarrassment.5
Anxiety can be managed by providing information to the patients about the procedure and all the steps that will be carried out, minimizing patient waiting time before the procedure, and maintaining constant verbal communication with the patient during the procedure (verbal anaesthesia).6 This kind of situation is not uncommon in gynecological practice in Europe and the solution there is to use office hysteroscopy with vaginoscopy. However,on the one hand this practice is still very rare in Indonesia, especially in Eastern Indonesia. Vaginoscopical access using a hysteroscope is still a rare and exclusive commodity in East Indonesia because the author’s center is the only one who has the tools and access to office hysteroscopy due to the high price of the equipment. On the other hand virginity itself is still a taboo and sacred thing in Indonesia, so for unmarried women this is something extremely valuable.
Material Method
The patient was given an analgesic suppository in an office setting. Vaginoscopy was performed with an Olympus hysteroscope with a working channel of 5French.
Case
A 36-year-old woman presented to the clinic with a complaint of abdominal discomfort and vaginal discharge from the vagina. The patient revealed that she masturbated using a ballpoint pen into her vagina in the morning and noticed that the ballpoint cap was left in her vagina.
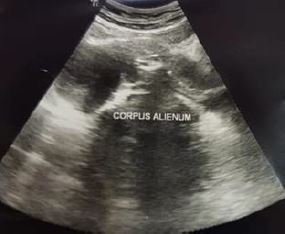
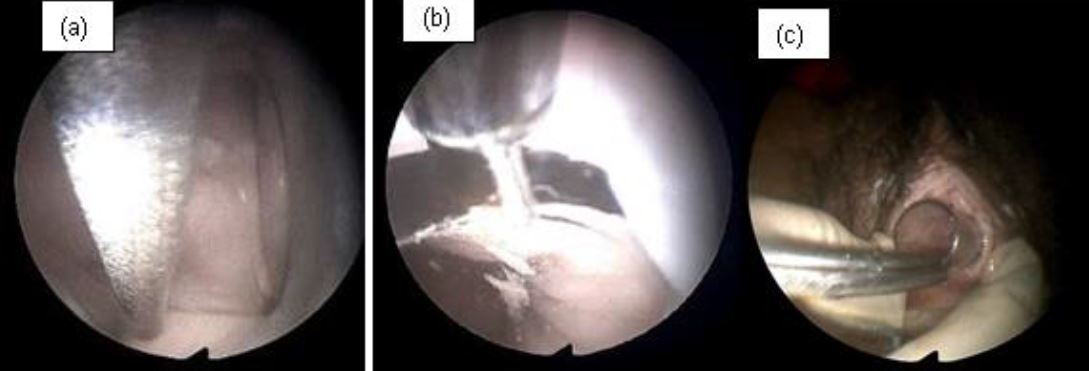
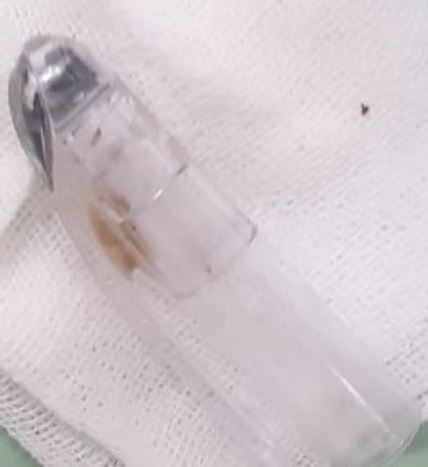
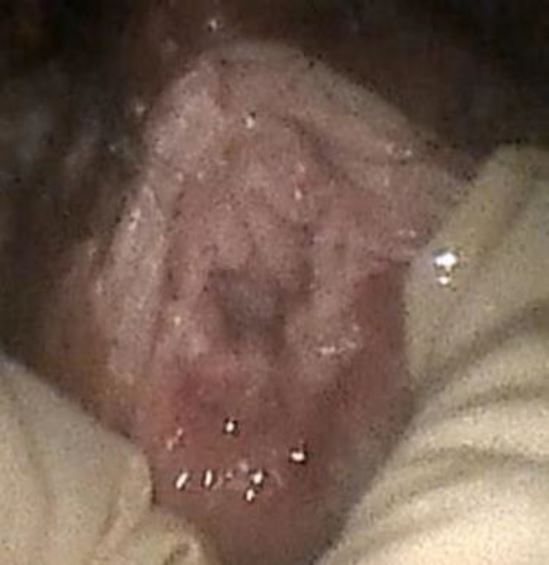
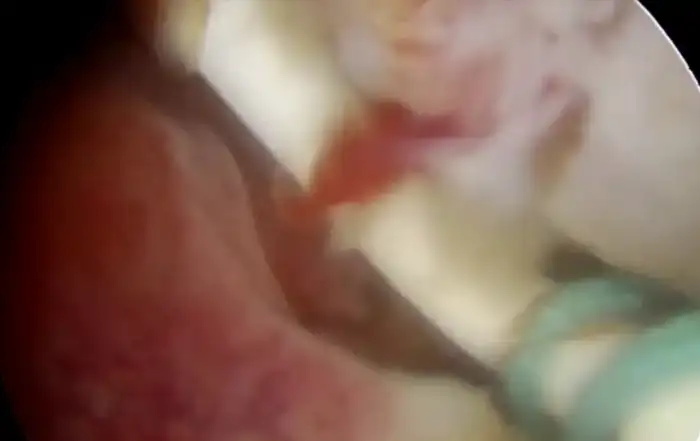
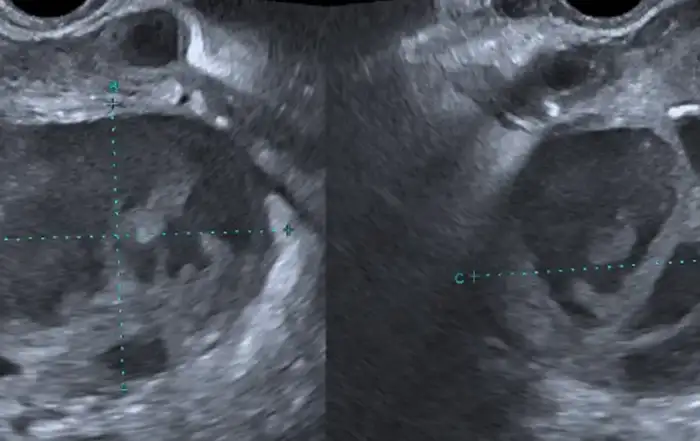
The patient came to the Obstetrics and Gynecology Specialist Private Clinic in her village the same morning. The OB-GYN doctor in the village had tried to extract the pen cap using a Hartmann alligator forceps but failed and he decided to refer the patient to the office hysteroscopy unit where vaginoscopy can be performed. Physical examination showed normal vital signs. The gynecological examination revealed that the hymen was intact with a whitish discharge. A colposcopy was not used to evaluate the hymen. Abdominal ultrasound showed that the ballpoint cap was in a horizontal position in front of the cervical portio (Figure 1). The only investigation that can be done is abdominal ultrasound because transvaginal ultrasonography cannot be performed considering the fact that the patient is still a virgin. The patient was given an analgesic suppository, and a vaginoscopy was performed to remove the ballpoint cap from the vagina. An Olympus hysteroscope with a working channel 5 French was used. The cap was stuck between vaginal walls in horizontal position. The cap’s position was shifted from horizontal to vertical position to avoid damaging the hymen. It was a quite difficult procedure but the cap was successfully removed (Figure 2). The pen cap, measured 50 x 8 x 8 mm (figure 4). The patient was discharged after the procedure the hymen remained intact.
Discussion
Virginity is a sensitive personal matter. Maintaining virginity is a personal importance and also depends on age, ethnicity, status, culture, and religion. As medical professionals, we have to respect that. However, there are times when a vaginal examination is necessary, which limits a gynecologist in making a diagnosis and approaching treatment. Hysteroscope can be used to observe the vagina for a diagnosis in cases of virgin patients. Vaginal discharge is the most common symptom of the vagina foreign body.7.8 Vaginal discharge may be purulent or hemorrhagic. The effect varies depending on its nature and shape. The various forms of the foreign body found in the vagina include clumps of toilet paper, marbles, beads, paper clips, lead. Pencils, sponges, plastics, and fibrous materials from clothing are often found in children. Pads, broken condoms, and objects not commonly used for masturbation are common foreign bodies found in the vagina in adolescents and adults. The foreign body of the vagina, which is mostly found in the elderly, is a pessary.7 Patients may self report a foreign body or have a variety of symptoms, such as pelvic pain, vaginal discharge, and vaginal bleeding. When evaluating a patient who is suspected of having a vaginal foreign body, the history should focus on the specifics surrounding the original occurrence, such as the timing, the suspected object, and abdominal, pelvic, and genital symptoms.2,8
This foreign body can cause perforation, abrasion, pressure necrosis, and local vaginitis resulting in ulceration of the vaginal wall. These effects involve adjacent structures, causing urinary and fecal fistulas. In severe cases, it may also cause salpingitis and peritonitis. Neglected foreign bodies in the vagina might lead to severe ulceration of the posterior fornix and subsequently to carcinoma of the vagina. The diagnosis can be made by a detailed history, genital examination, pelvic ultrasound, pelvic radiography, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).10,11 MRI is considered the best technique for evaluating the vaginal foreign body, but it is not always available in the office setting. Vaginoscopy with a 5 mm hysteroscope is useful for detecting and treating the vaginal foreign body.10 The patient in our case was unmarried and still a virgin. The considerations for a diagnosis and management should include the potential for hymenal tissue disruption. Vaginoscopy can be an appropriate diagnostic and management tool in this case.10
The vaginoscopy approach with a hysteroscope provides a safe and non-traumatic method of assessing the reproductive organs because the hysteroscope can be inserted into the vagina without a speculum or tenaculum.2.5 Vaginal wall distention by distension media can provide a clear endoscopic view. These considerations make doctors choose this procedure in assessing the pathology of the vagina, cervical surface, cervical canal, intrauterine cavity, and other anomalies of the development of sex organs in pediatric, adolescent, or female patients who are still virgins. The entire procedure can be performed without compromising the integrity of the hymen, whereas traditional methods require the use of retractors which may compromise the integrity of the hymen.2 However, unlike in developed countries, hysteroscopy procedures and hysteroscope instruments are still uncommon in Indonesia, especially in the East Indonesia region. In most developing countries, hysteroscope instruments are still considered a luxury and are not readily available in daily practice, even in private clinics or hospitals. Vaginoscopy is the recommended standard technique.5 Small diameter hysteroscopes together with vaginoscopy techniques have contributed to outpatient procedures in private clinics without the use of analgesics. The procedure is declared a proper and safe procedure to be applied in practice.12 Any endoscope with irrigation properties can be used for vaginoscopy. A bronchoscope or urethroscope is ideal because of its short length; a laparoscope, cystoscope, nephroscope, or hysteroscope can also be used. A very small diameter hysteroscope is required for gynecological examination in the case of young children.13 Vaginoscopy procedure is performed in the lithotomy position. Without using speculum, a small (5 mm) rigid or semi-rigid hysteroscope is inserted into the vaginal introitus. Normal saline is administered as a distension medium at a pressure of 150 mmHg. The labia minora are closed manually if necessary to accommodate the distension media. The cervix is visualized, and the hysteroscope is directed through the vaginal introitus to the anterior portion.9 The ideal management of the vaginal foreign is to remove it from the vaginal canal.14 The. Unlike the practices in the developed countries, removal by office hysteroscopy in Indonesia without damaging the hymen is still uncommon. Complication such as damaged hymen is still common in Indonesia. In this case, the foreign body was removed by vaginoscopy with hysteroscope and suppository analgesics. We shifted the position of the ballpoint cap from a horizontal to a vertical position to avoid damaging the hymen. It was then successfully removed without damaging the hymen. Analgesia is useful for reducing pain.6 Analgesic method is the key in performing vaginoscopy in a painless practice.15
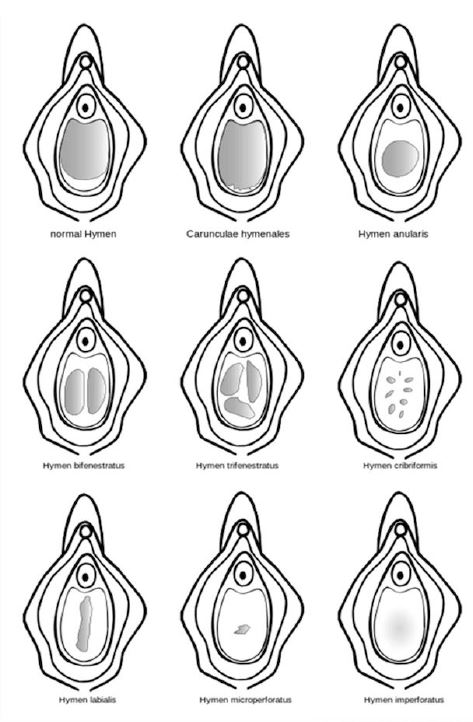
The advantages of using office vaginoscopy over conventional vaginoscopy include a lower rate of pain, shorter examination time, and greater success rate.16.17 These advantages make vaginoscopy the technique of choice for outpatient hysteroscopy.17 The advantage of using vaginoscopy in the private clinic consists of reduced patient care costs, and reduced burden on health care budgets in general.18 Despite the advantages, vaginoscopy carries a risk of genital tract infection in patients undergoing vaginoscopy, which is associated with procedures without adequate pre-procedural disinfection.16 Without analgesia, the use of vaginoscopy in the private clinics can cause excessive discomfort, severe pain, high anxiety, and shame for the patient, which may lead to failure of the procedure.5 The use of analgesia can relieve pain, and non-pharmacological methods can also be useful in reducing pain in private clinical settings vaginoscopy procedures such as reducing waiting times, and using music during procedures to reduce anxiety.15 The hymen’s shape, size, and flexibility fluctuate dramatically throughout a woman’s lifetime. The and hymenal suppleness increases. Additional alterations occur as a result of hormonal changes associated being “broken” are often assumed indications of virginity in cultures where female virginity before pale pink in color, there were no lacerations, clefts, perforations, blood. It happened due to elasticity of the hymen in accordance with the theory described, the type of hymen in patients with annular shape (figure 4)
Conclusion
Vaginoscopy in a office setting without anesthesia is useful as a diagnostic method for managing the vaginal foreign body without damaging the hymen. Non-pharmacological methods can be considered to increase the success of the procedure by reducing pain and anxiety during the procedure.
References
Olympus hysteroscope with a working channel of 5French
Figure 1. Ultrasound results show foreign body inside vaginal introitus
Figure 2. Vaginoscopy
a.Ballpoint cap stuck between vagina wall in horizontal position
b.The ballpoint cap was successfully shifted from a horizontal position to a vertical position
c.The ballpoint cap was successfully removed
Figure 3. Ballpoint cap successfully extracted
Figure 4. Appearance of vaginal hymen after extraction
Addendum: Different configuration of Hymen